Hello...guyz..! welcome back my tutorials friends today I will discuss Inter VLAN Routing and Router-On-stick.
let's understand that what do u means these Routing.
Inter VLAN Routing:- A method that is used to communicate different VLAN of the subnet.
In this method, we use a layer 3 device. Such as Roter.
Once a host is separated through the VLAN, member host of the same VLAN can communication
with each other.
Configuration Inter VLAN Routing,
first of all, go to the router and command is
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#interface f0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface f0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
after that go to switch here command is
Switch(config)#vlan 10
Switch(config-vlan)#vlan 20
Switch(config-vlan)#exit
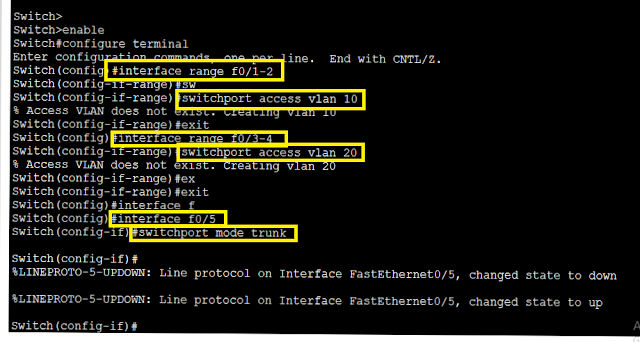
Switch(config)#interface range fastEthernet 0/1-2
Switch(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 10
Switch(config-if-range)#exit
Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/6
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
Switch(config-if)#exit
Switch(config)#interface range fastEthernet 0/3-4
Switch(config-if-range)#switchport access vlan 20
Switch(config-if-range)#exit
Switch(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/5
Switch(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20
Switch(config-if)#exit
Router-on-stick:- It is the second method is if we want to communicate different VLAN of the subnet here is also required layer 3 device such as Router.
The process of connecting one physical link with the trunked logical(sub) interface is known as Router-on-stick.
Configuration of Router-on-stick
the command is
go to on router
(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(go to on router
Router>enable
Router#configure termianl
Router(config)#interface f0/0
Routerconfig-if)#exit
Router(config)#interface f0/0.10
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 10
Router(config-subif)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-subif)#no shutdown
Router(config-subif)#exit
Router(config)#interface f0/0.20
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1Q 20
Router(config-subif)#ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
Router(config-subif)#no shutdown
Router(config-subif)#exit
after that go switch